- Explore MCP Servers
- MCP-Demo
Mcp Demo
What is Mcp Demo
MCP-Demo is a demonstration project showcasing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) through weather forecasting and time services. It provides a practical implementation of MCP-compliant tools.
Use cases
Use cases include integrating weather forecasts into mobile applications, providing time information for global events, and developing web applications that utilize LLMs for enhanced user interaction.
How to use
To use MCP-Demo, set up the weather and time servers by running their respective Python scripts. You can access the services via the web UI or through the HTTP bridge that exposes the MCP tools as REST APIs.
Key features
Key features include an MCP-compliant weather server with forecasting capabilities, a time server with geocoding and timezone detection, a generic HTTP bridge for REST API integration, and a web UI that connects to Ollama LLM with automatic tool routing.
Where to use
MCP-Demo can be used in various fields such as weather forecasting applications, time management systems, and any web applications that require real-time data integration.
Clients Supporting MCP
The following are the main client software that supports the Model Context Protocol. Click the link to visit the official website for more information.
Overview
What is Mcp Demo
MCP-Demo is a demonstration project showcasing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) through weather forecasting and time services. It provides a practical implementation of MCP-compliant tools.
Use cases
Use cases include integrating weather forecasts into mobile applications, providing time information for global events, and developing web applications that utilize LLMs for enhanced user interaction.
How to use
To use MCP-Demo, set up the weather and time servers by running their respective Python scripts. You can access the services via the web UI or through the HTTP bridge that exposes the MCP tools as REST APIs.
Key features
Key features include an MCP-compliant weather server with forecasting capabilities, a time server with geocoding and timezone detection, a generic HTTP bridge for REST API integration, and a web UI that connects to Ollama LLM with automatic tool routing.
Where to use
MCP-Demo can be used in various fields such as weather forecasting applications, time management systems, and any web applications that require real-time data integration.
Clients Supporting MCP
The following are the main client software that supports the Model Context Protocol. Click the link to visit the official website for more information.
Content
MCP Docker Demo
A Docker-based demonstration of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) with weather forecasting and time services.
Project Overview
This project demonstrates how to build and deploy MCP-compliant tools using Docker containers. It showcases a complete web application architecture with:
- MCP Weather Tool - Provides weather forecasts for any location
- MCP Time Tool - Returns current time and timezone information
- HTTP Bridge Service - Translates between web requests and MCP protocol
- Web Frontend - Browser interface with Ollama LLM integration and intelligent tool routing
Quick Start
-
Ensure prerequisites are installed and running:
# Verify Docker is running docker info # Verify Ollama is running with at least one model curl http://localhost:11434/api/tags # You should see a list of available modelsIf Docker is not running, start Docker Desktop.
If Ollama is not running, start it and pull at least one model:ollama run llama2 # Or any other model you prefer -
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/AITrekker/MCP-Demo.git cd MCP-Demo -
Start the services:
docker-compose up --build -
Open the web interface:
http://localhost:8080/mcp_host.html -
Try example queries:
- “What’s the weather in Seattle?”
- “What time is it in Tokyo?”
- “Tell me about quantum physics” (falls back to LLM)
Architecture
Browser → Frontend Container → MCP Server Container → MCP Tools ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ HTML/JS (Port 8080) (Port 5000) Python Scripts
The system uses a microservices architecture where:
- Frontend Container: Serves the web interface
- MCP Server Container: Hosts the Flask API and executes MCP tools
- MCP Tools: Run as subprocesses within the MCP server container
Screenshots
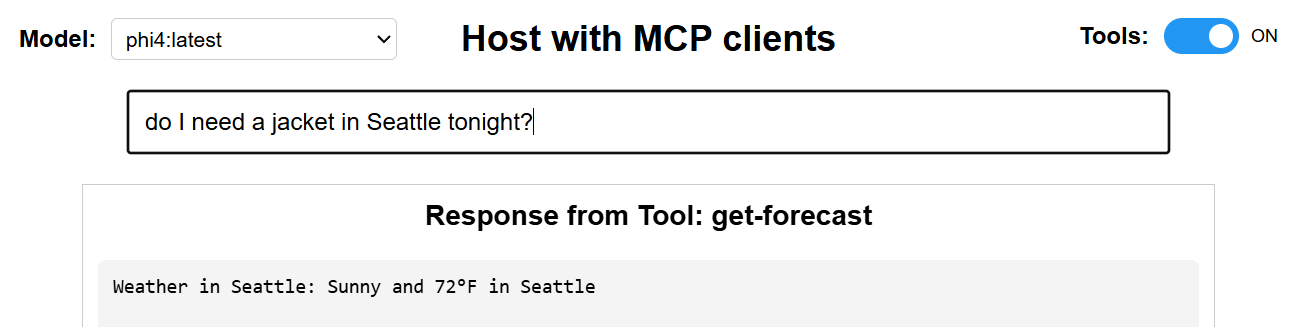
Time Tool Example

Weather Tool Example
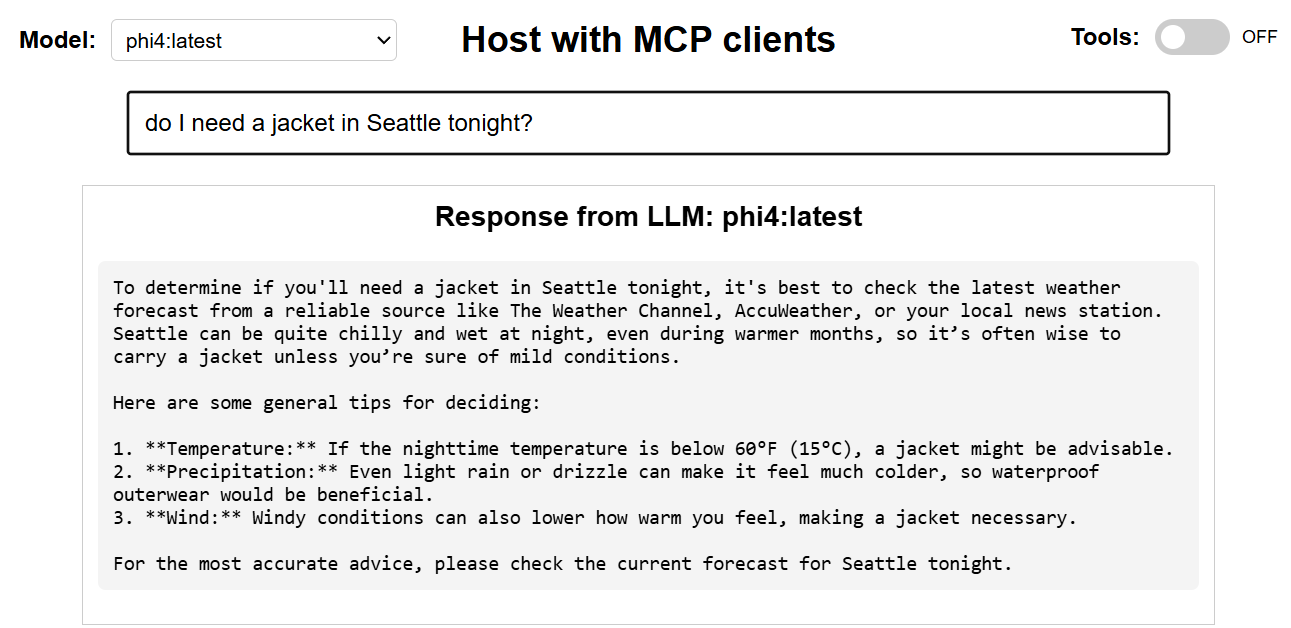
LLM Fallback with No Tools
Project Structure
MCP-Demo/ ├── mcp-server/ │ ├── Dockerfile │ └── server.py # Flask HTTP MCP server ├── frontend/ │ ├── Dockerfile │ ├── mcp_host.html # Web interface │ └── styles.css # Styling ├── weather-tool/ │ └── tool.py # MCP weather tool ├── time-tool/ │ └── tool.py # MCP time tool ├── docker-compose.yml # Container orchestration └── README.md
Components
MCP Server (mcp-server/server.py)
A Flask-based HTTP server that acts as an intermediary between web browsers and MCP tools:
- Receives HTTP POST requests with JSON payloads
- Translates them into MCP protocol format
- Executes MCP tools as subprocesses via stdin/stdout
- Returns formatted JSON responses to the browser
- Handles CORS for browser compatibility
Weather Tool (weather-tool/tool.py)
An MCP-compliant tool that provides weather forecasts:
- Uses wttr.in API for weather data
- Falls back to mock data if API is unavailable
- Follows MCP protocol for stdin/stdout communication
- Implements the
get-forecasttool
Time Tool (time-tool/tool.py)
An MCP-compliant tool that provides time information:
- Uses OpenStreetMap for geocoding locations
- Estimates timezones based on geographical coordinates
- Implements the
get-timetool - Returns local time, date, and timezone information
Web Frontend (frontend/mcp_host.html)
A responsive web interface that provides:
- Model selection from available Ollama models
- Toggle switch for enabling/disabling tools
- LLM-based intelligent tool routing - Uses the selected LLM to analyze user queries and determine which tool to use
- Automatic parameter extraction from natural language queries
- Fallback to LLM for general queries that don’t require tools
- Clear attribution of response sources (Tool vs LLM)
The new intelligent routing system understands various ways users might request tool functionality:
- “What’s the weather like in Paris?” → Weather tool
- “Can you tell me the current time in Tokyo?” → Time tool
- “How do I learn Python?” → LLM response
Getting Started
Prerequisites
Development Mode
For faster development iterations, you can restart individual services:
# Restart frontend only (for HTML/CSS changes)
docker-compose restart frontend
# Rebuild and restart mcp-server (for Python changes)
docker-compose build mcp-server
docker-compose up
How It Works
Query Flow
- User Input: User types a natural language query in the web interface
- LLM Analysis: The selected LLM analyzes the query to determine if it requires a specific tool
- Parameter Extraction: If a tool is needed, the LLM extracts relevant parameters (like location)
- Tool Execution: The appropriate MCP tool is called via the HTTP bridge service
- MCP Protocol: Bridge translates HTTP to MCP format and executes the tool
- Response: Tool output is returned through the bridge to the browser
- LLM Fallback: If no tool is needed or confidence is low, query goes directly to Ollama
Intelligent Tool Selection
The system now uses LLM-based analysis instead of rigid pattern matching:
User Query: "What's the weather like in London today?" ↓ LLM Analysis: {"tool": "get-forecast", "location": "London", "confidence": 0.95} ↓ Tool Execution: Weather API call for London ↓ Response: "Weather in London: Cloudy and 64°F in London"
This approach handles natural language variations much better than regex patterns:
- “Weather in Seattle?” ✓
- “How’s the climate in Tokyo right now?” ✓
- “Is it raining in Paris?” ✓
- “Current atmospheric conditions for New York?” ✓
MCP Protocol Translation
HTTP Request: {"location": "Seattle"} ↓ MCP Format: {"type": "tool-call", "tool": "get-forecast", "input": {"location": "Seattle"}} ↓ MCP Response: {"type": "tool-result", "output": {"location": "Seattle", "forecast": "..."}} ↓ HTTP Response: {"location": "Seattle", "forecast": "..."}
Troubleshooting
Docker Authentication Issues
If you encounter Docker authentication errors like 401 Unauthorized when pulling images:
# Ensure you're logged in to Docker Hub
docker login
# Pre-pull required images before building
docker pull python:3.11-slim
docker pull nginx:alpine
# Try building again
docker-compose up --build
Sometimes restarting Docker Desktop can also resolve authentication issues.
Common Issues
- “Failed to fetch” errors: Ensure Ollama is running on port 11434
- Tool execution errors: Check Docker logs with
docker-compose logs bridge - Frontend not loading: Verify the frontend container is running on port 8080
Viewing Logs
# View all logs
docker-compose logs
# View specific service logs
docker-compose logs bridge
docker-compose logs frontend
API Testing
You can test the bridge service directly using curl:
# Test weather endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/weather \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"location":"Seattle"}'
# Test time endpoint
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/time \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"location":"Tokyo"}'
Configuration
Port Configuration
- Frontend:
8080(configurable in docker-compose.yml) - Bridge:
5000(configurable in docker-compose.yml) - Ollama:
11434(default Ollama port on host machine)
Adding New Tools
To add a new MCP tool:
- Create a new directory (e.g.,
calculator-server/) - Implement your tool following the MCP protocol (see existing tools as examples)
- Add the tool directory to the bridge container in
bridge/Dockerfile - Add a new endpoint in
bridge/bridge.py - Add pattern matching in the frontend HTML
License
MIT
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! This demo provides a foundation for exploring the Model Context Protocol with Docker. Some areas for expansion:
Potential New Tools
- Calculator Tool: Mathematical computations
- File Search Tool: Search local filesystem
- API Client Tool: Generic REST API client
- Database Query Tool: Simple database operations
Enhancement Ideas
- Tool Discovery: Dynamic tool registration and discovery
- Authentication: Add API key management
- Monitoring: Add health checks and metrics
- Performance: Implement tool response caching
Contribution Steps
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/new-tool) - Implement your changes following the existing patterns
- Test with Docker Compose
- Update documentation
- Submit a pull request
For questions or discussions about MCP integration patterns, feel free to open an issue!
DevTools Supporting MCP
The following are the main code editors that support the Model Context Protocol. Click the link to visit the official website for more information.










