- Explore MCP Servers
- blender
Blender
What is Blender
BlenderMCP is an integration that connects Blender, a powerful 3D modeling software, with Claude AI using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This integration enables Claude to assist users in creating and manipulating 3D models and scenes within Blender, enhancing the modeling experience with AI-driven prompts.
Use cases
Users can leverage BlenderMCP for various tasks such as generating low-poly models, creating intricate scenes, modifying existing objects, applying textures and materials, and even executing custom Python scripts in Blender. Practical applications include designing game assets, concept art, architectural visualizations, and experimental 3D art.
How to use
To utilize BlenderMCP, users need to install the addon.py file in Blender, configure the MCP server settings in Claude desktop, and establish a connection through the Blender interface. Users can then issue commands to Claude to perform specific actions like creating or modifying objects, downloading assets, or generating scenes based on given prompts.
Key features
Key features of BlenderMCP include two-way communication between Claude and Blender, object manipulation capabilities, control over materials, scene inspection, and the ability to execute Python code within Blender. Additionally, it integrates with Poly Haven for asset downloads and Hyper3D for AI-generated models.
Where to use
BlenderMCP is suitable for 3D artists, game developers, and designers who utilize Blender for modeling and scene creation. It can be used in various environments such as studios, educational settings, and individual projects where a blend of AI assistance and traditional modeling techniques improves productivity.
Overview
What is Blender
BlenderMCP is an integration that connects Blender, a powerful 3D modeling software, with Claude AI using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This integration enables Claude to assist users in creating and manipulating 3D models and scenes within Blender, enhancing the modeling experience with AI-driven prompts.
Use cases
Users can leverage BlenderMCP for various tasks such as generating low-poly models, creating intricate scenes, modifying existing objects, applying textures and materials, and even executing custom Python scripts in Blender. Practical applications include designing game assets, concept art, architectural visualizations, and experimental 3D art.
How to use
To utilize BlenderMCP, users need to install the addon.py file in Blender, configure the MCP server settings in Claude desktop, and establish a connection through the Blender interface. Users can then issue commands to Claude to perform specific actions like creating or modifying objects, downloading assets, or generating scenes based on given prompts.
Key features
Key features of BlenderMCP include two-way communication between Claude and Blender, object manipulation capabilities, control over materials, scene inspection, and the ability to execute Python code within Blender. Additionally, it integrates with Poly Haven for asset downloads and Hyper3D for AI-generated models.
Where to use
BlenderMCP is suitable for 3D artists, game developers, and designers who utilize Blender for modeling and scene creation. It can be used in various environments such as studios, educational settings, and individual projects where a blend of AI assistance and traditional modeling techniques improves productivity.
Content
BlenderMCP - Blender Model Context Protocol Integration
BlenderMCP connects Blender to Claude AI through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing Claude to directly interact with and control Blender. This integration enables prompt assisted 3D modeling, scene creation, and manipulation.
Join the Community
Give feedback, get inspired, and build on top of the MCP: Discord
Supporters
Top supporters:
All supporters:
Release notes (1.2.0)
- View screenshots for Blender viewport to better understand the scene
- Search and download Sketchfab models
Previously added features:
- Support for Poly Haven assets through their API
- Support to generate 3D models using Hyper3D Rodin
- For newcomers, you can go straight to Installation. For existing users, see the points below
- Download the latest addon.py file and replace the older one, then add it to Blender
- Delete the MCP server from Claude and add it back again, and you should be good to go!
Features
- Two-way communication: Connect Claude AI to Blender through a socket-based server
- Object manipulation: Create, modify, and delete 3D objects in Blender
- Material control: Apply and modify materials and colors
- Scene inspection: Get detailed information about the current Blender scene
- Code execution: Run arbitrary Python code in Blender from Claude
Components
The system consists of two main components:
- Blender Addon (
addon.py): A Blender addon that creates a socket server within Blender to receive and execute commands - MCP Server (
src/blender_mcp/server.py): A Python server that implements the Model Context Protocol and connects to the Blender addon
Installation
Prerequisites
- Blender 3.0 or newer
- Python 3.10 or newer
- uv package manager:
If you’re on Mac, please install uv as
brew install uv
On Windows
powershell -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
and then
set Path=C:\Users\nntra\.local\bin;%Path%
Otherwise installation instructions are on their website: Install uv
⚠️ Do not proceed before installing UV
Claude for Desktop Integration
Watch the setup instruction video (Assuming you have already installed uv)
Go to Claude > Settings > Developer > Edit Config > claude_desktop_config.json to include the following:
{
"mcpServers": {
"blender": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"blender-mcp"
]
}
}
}Cursor integration
For Mac users, go to Settings > MCP and paste the following
- To use as a global server, use “add new global MCP server” button and paste
- To use as a project specific server, create
.cursor/mcp.jsonin the root of the project and paste
{
"mcpServers": {
"blender": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"blender-mcp"
]
}
}
}For Windows users, go to Settings > MCP > Add Server, add a new server with the following settings:
{
"mcpServers": {
"blender": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": [
"/c",
"uvx",
"blender-mcp"
]
}
}
}⚠️ Only run one instance of the MCP server (either on Cursor or Claude Desktop), not both
Installing the Blender Addon
- Download the
addon.pyfile from this repo - Open Blender
- Go to Edit > Preferences > Add-ons
- Click “Install…” and select the
addon.pyfile - Enable the addon by checking the box next to “Interface: Blender MCP”
Usage
Starting the Connection
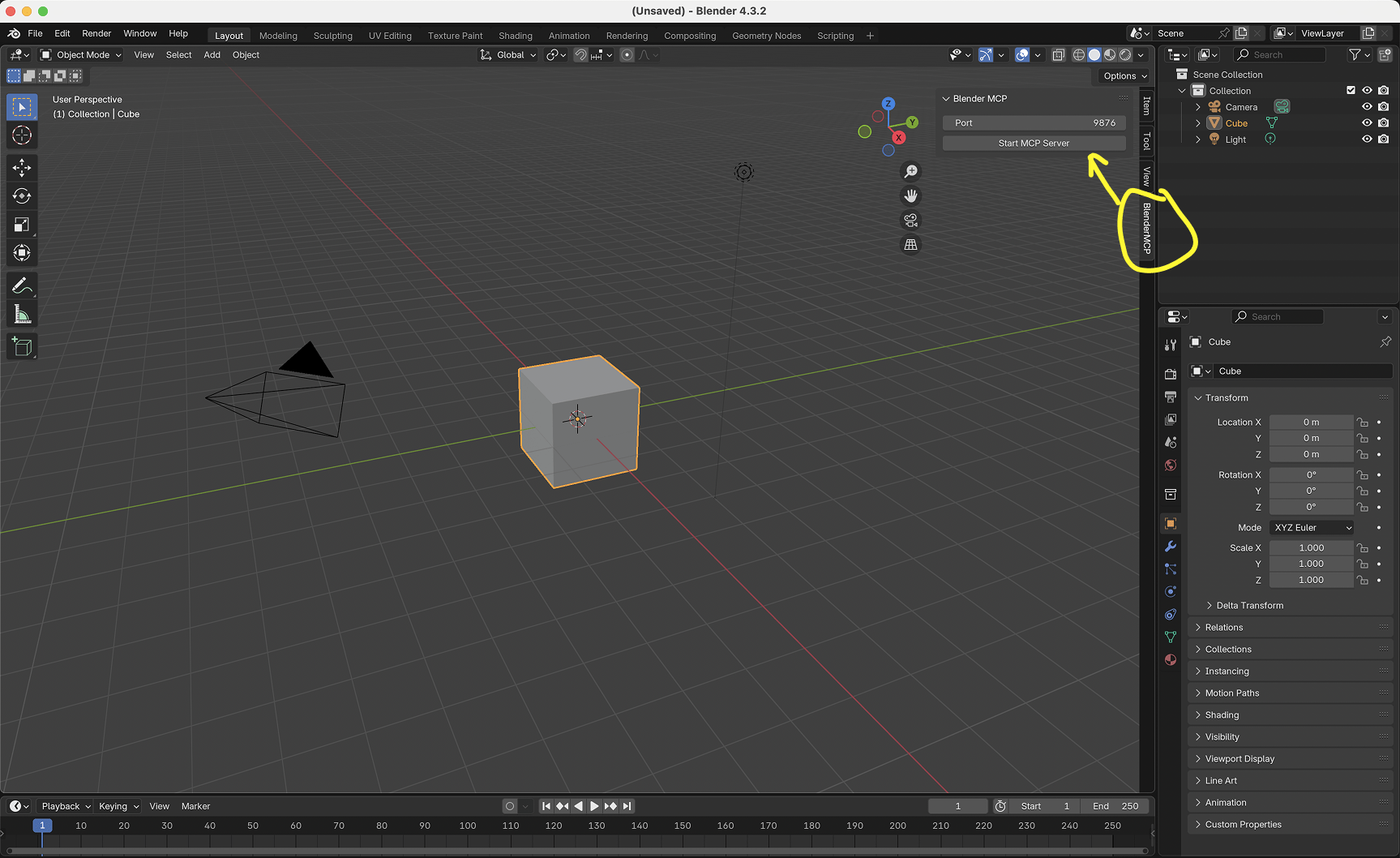
- In Blender, go to the 3D View sidebar (press N if not visible)
- Find the “BlenderMCP” tab
- Turn on the Poly Haven checkbox if you want assets from their API (optional)
- Click “Connect to Claude”
- Make sure the MCP server is running in your terminal
Using with Claude
Once the config file has been set on Claude, and the addon is running on Blender, you will see a hammer icon with tools for the Blender MCP.
![]()
Capabilities
- Get scene and object information
- Create, delete and modify shapes
- Apply or create materials for objects
- Execute any Python code in Blender
- Download the right models, assets and HDRIs through Poly Haven
- AI generated 3D models through Hyper3D Rodin
Example Commands
Here are some examples of what you can ask Claude to do:
- “Create a low poly scene in a dungeon, with a dragon guarding a pot of gold” Demo
- “Create a beach vibe using HDRIs, textures, and models like rocks and vegetation from Poly Haven” Demo
- Give a reference image, and create a Blender scene out of it Demo
- “Generate a 3D model of a garden gnome through Hyper3D”
- “Get information about the current scene, and make a threejs sketch from it” Demo
- “Make this car red and metallic”
- “Create a sphere and place it above the cube”
- “Make the lighting like a studio”
- “Point the camera at the scene, and make it isometric”
Hyper3D integration
Hyper3D’s free trial key allows you to generate a limited number of models per day. If the daily limit is reached, you can wait for the next day’s reset or obtain your own key from hyper3d.ai and fal.ai.
Troubleshooting
- Connection issues: Make sure the Blender addon server is running, and the MCP server is configured on Claude, DO NOT run the uvx command in the terminal. Sometimes, the first command won’t go through but after that it starts working.
- Timeout errors: Try simplifying your requests or breaking them into smaller steps
- Poly Haven integration: Claude is sometimes erratic with its behaviour
- Have you tried turning it off and on again?: If you’re still having connection errors, try restarting both Claude and the Blender server
Technical Details
Communication Protocol
The system uses a simple JSON-based protocol over TCP sockets:
- Commands are sent as JSON objects with a
typeand optionalparams - Responses are JSON objects with a
statusandresultormessage
Limitations & Security Considerations
- The
execute_blender_codetool allows running arbitrary Python code in Blender, which can be powerful but potentially dangerous. Use with caution in production environments. ALWAYS save your work before using it. - Poly Haven requires downloading models, textures, and HDRI images. If you do not want to use it, please turn it off in the checkbox in Blender.
- Complex operations might need to be broken down into smaller steps
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
Disclaimer
This is a third-party integration and not made by Blender. Made by Siddharth
