- Explore MCP Servers
- joinly
Joinly
Overview
What is Joinly
Joinly is a platform designed to make meetings accessible for AI agents, enabling them to participate and extract valuable insights from discussions.
Use cases
Use cases for Joinly include enhancing remote team meetings, providing accessibility for participants with disabilities, and generating meeting summaries for better follow-up.
How to use
To use Joinly, users can integrate it with their meeting platforms, allowing AI agents to join meetings, listen, and analyze the conversation in real-time.
Key features
Key features of Joinly include real-time transcription, AI-driven insights, seamless integration with popular meeting tools, and customizable settings for different meeting types.
Where to use
Joinly can be used in various fields such as corporate environments, educational institutions, and remote teams that require effective communication and collaboration.
Content
Make your meetings accessible to AI Agents 🤖
joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to join and actively participate in video calls. Through its MCP server, joinly.ai provides essential meeting tools and resources that can equip any AI agent with the skills to perform tasks and interact with you in real time during your meetings.
Want to dive right in? Jump to the Quickstart!
Want to know more? Visit our website!
:sparkles: Features
- Live Interaction: Lets your agents execute tasks and respond in real-time by voice or chat within your meetings
- Conversational flow: Built-in logic that ensures natural conversations by handling interruptions and multi-speaker interactions
- Cross-platform: Join Google Meet, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams (or any available over the browser)
- Bring-your-own-LLM: Works with all LLM providers (also locally with Ollama)
- Choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT: Modular design supports multiple services - Whisper/Deepgram for STT and Kokoro/Deepgram for TTS (and more to come…)
- 100% open-source, self-hosted and privacy-first :rocket:
:video_camera: Demos
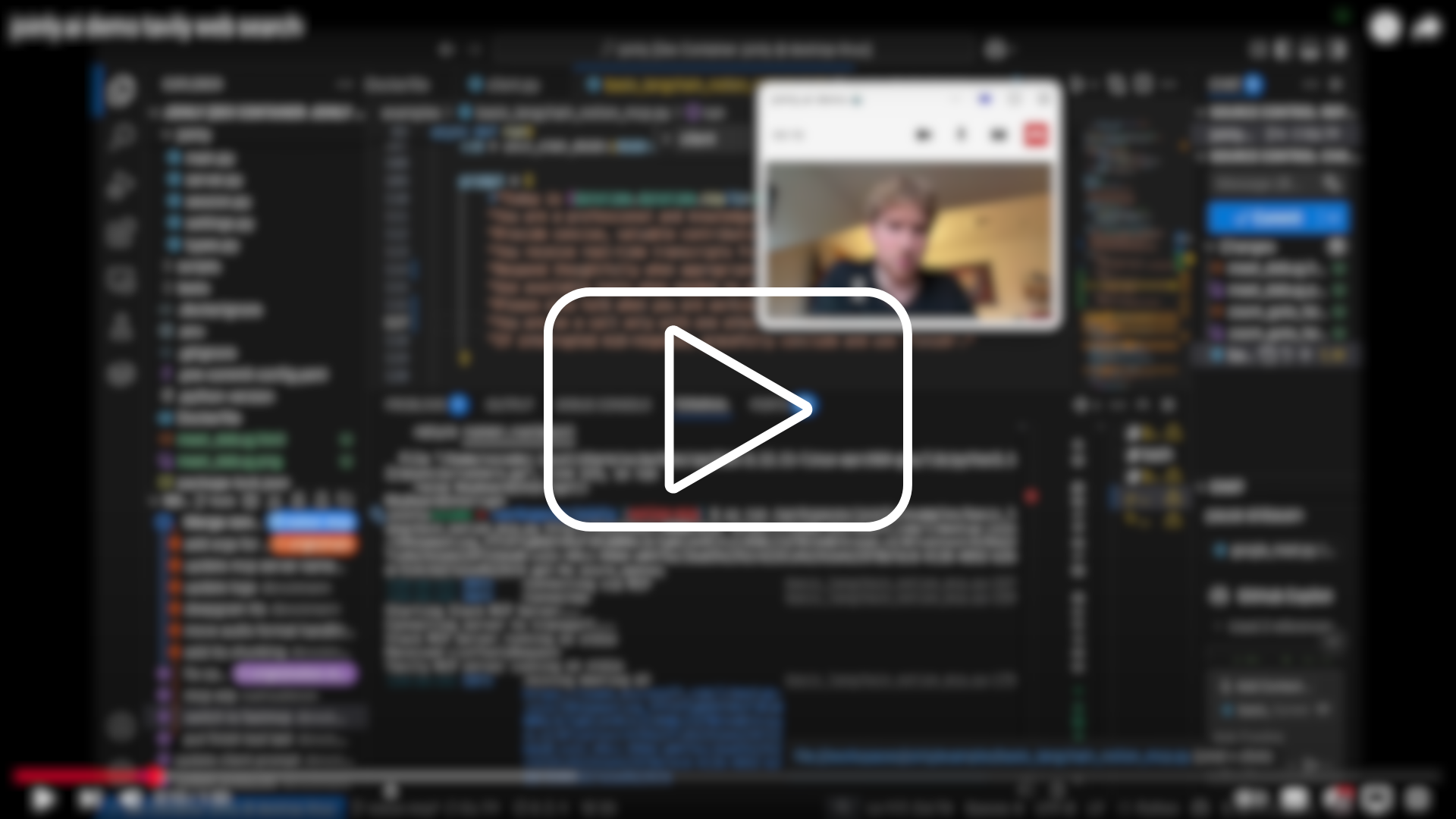
Websearch
In this demo video, you can see joinly anwsering simple questions by accessing the latest news from the web.
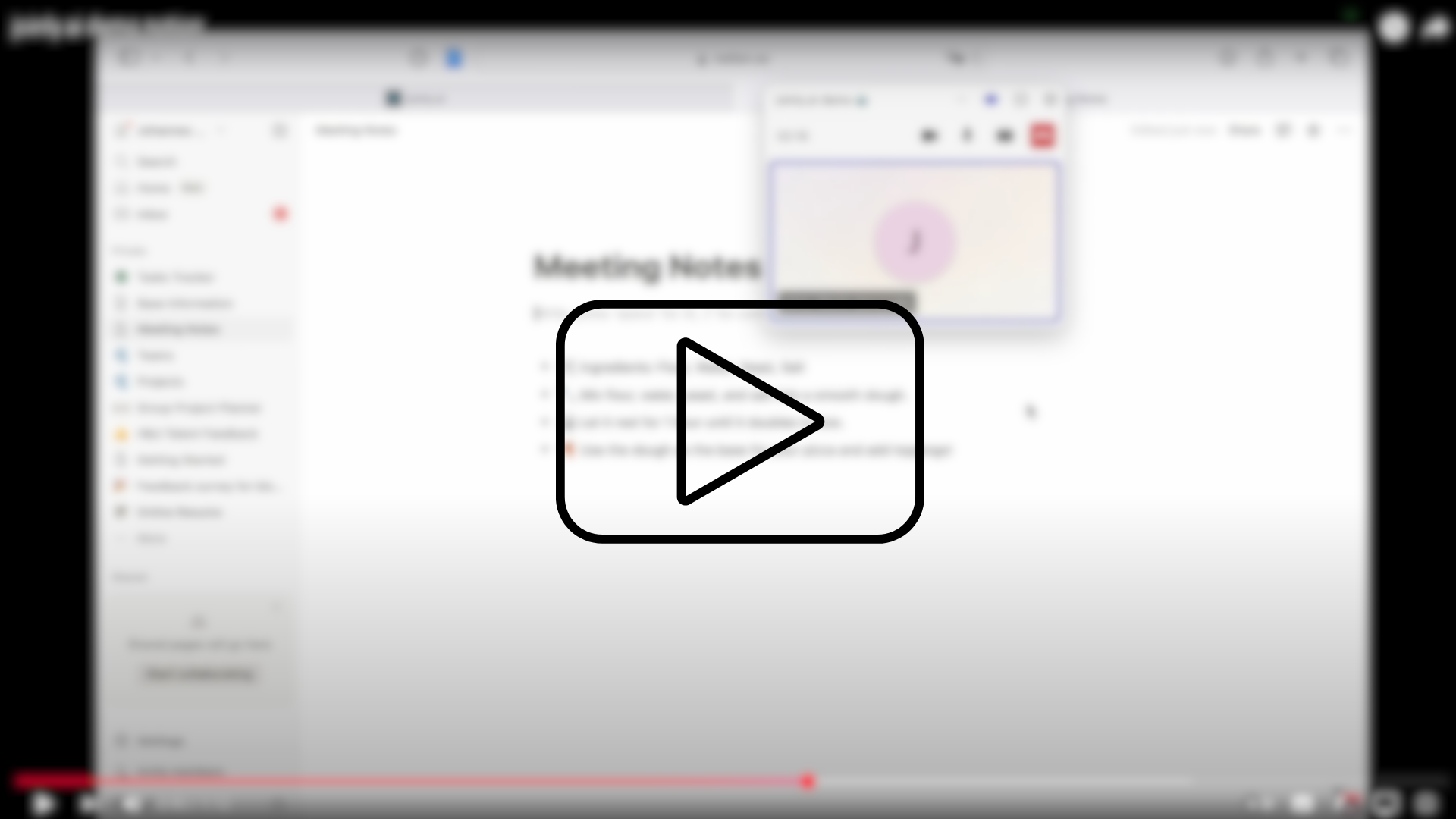
Notion
In this demo video, we connect joinly to our notion via MCP and let it edit the content of a page content live in the meeting.
Any ideas what we should build next? Write us! :rocket:
:zap: Quickstart
Run joinly via Docker with a basic conversational agent client.
[!IMPORTANT]
Prerequisites: Docker installation
Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/joinly-ai/joinly
cd joinly
Create a new .env file in the project root with your API keys. See .env.example for complete configuration options including Anthropic (Claude) and Ollama setups. Replace the placeholder values with your actual API keys and adjust the model name as needed.
[!NOTE]
Remember not to copy the .env.example exactly. Instead, delete the placeholder values of the providers you don’t use.
# .env # for OpenAI LLM # change key and model to your desired one JOINLY_MODEL_NAME=gpt-4o JOINLY_MODEL_PROVIDER=openai OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key
[!TIP]
You can find the OpenAI API key here
Pull the Docker image (~2.3GB since it packages browser and models):
docker pull ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest
Launch your meeting in Zoom, Google Meet or Teams and let joinly join the meeting using the meeting link as <MeetingURL>:
docker run --env-file .env ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest -v --client <MeetingURL>
:red_circle: Having trouble getting started? Let’s figure it out together on our discord!
:technologist: Run an external client
In Quickstart, we ran the Docker Container directly as a client using --client. But we can also run it as a server and connect to it from outside the container, which allows us to control the entire logic of our agent. Here, we run an external client implementation and connect it to the joinly MCP server.
[!IMPORTANT]
Prerequisites: do the Quickstart (except the last command), install uv, and open two terminals
Start the joinly server in the first terminal (note, we are not using --client here and forward port 8000):
docker run --env-file .env -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly:latest -v
While the server is running, start the example client implementation in the second terminal window to connect to it and join a meeting:
uv run examples/client_example.py --mcp-url http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp/ <MeetingUrl>
Add MCP servers to the client
Add the tools of any MCP server to the example client by providing a JSON configuration. In config_tavily.json, we add the Tavily MCP server for web search functionality (requires TAVILY_API_KEY in .env):
{
"mcpServers": {
"tavily": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"[email protected]"
]
}
}
}You can also add multiple entries under "mcpServers" which will all be available as tools in the meeting (see fastmcp client docs for config syntax). Then, run the client using the config file (--config <file>):
uv run examples/client_example.py --mcp-url http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp/ --config examples/config_tavily.json <MeetingUrl>
:wrench: Configurations
# Start server (default), connect via own client
uv run joinly
# Start directly as client
uv run joinly --client <MeetingUrl>
# Change name (default: joinly)
uv run joinly --name "AI Assistant"
# Change TTS provider
uv run joinly --tts kokoro # default: local Kokoro
uv run joinly --tts deepgram # include DEEPGRAM_API_KEY in your .env
# Change Transcription (STT) provider
uv run joinly --stt whisper # default: local Whisper (faster-whisper)
uv run joinly --stt deepgram # include DEEPGRAM_API_KEY in your .env
# Change host & port of the joinly MCP server
uv run joinly --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
# Start browser with a VNC server for debugging;
# forward the port and connect to it using a VNC client
uv run joinly --vnc-server --vnc-server-port 5900
# Use browser agent as fallback/to join any meeting website (Experimental)
# Note: this requires npx (not installed in the docker but in devcontainer),
# LLM is selected using the same ENV variables as described earlier
uv run joinly --browser-agent playwright-mcp
# Logging
uv run joinly -v # or -vv, -vvv
# Help
uv run joinly --help
GPU Support
We provide a Docker image with CUDA GPU support for running the transcription and TTS models on a GPU. To use it, you need to have the NVIDIA Container Toolkit installed and CUDA >= 12.6. Then pull the CUDA-enabled image:
docker pull ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly-cuda:latest
Run as client or server with the same commands as above, but use the joinly-cuda image and set --gpus all:
# Run as server
docker run --gpus all --env-file .env -p 8000:8000 ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly-cuda:latest -v
# Run as client
docker run --gpus all --env-file .env ghcr.io/joinly-ai/joinly-cuda:latest -v --client <MeetingURL>
By default, the joinly image uses the Whisper model base.en for transcription, since it still runs reasonably fast on CPU. For joinly-cuda, it automatically defaults to distil-large-v3 for significantly better transcription quality. You can change the model by setting --stt-arg model_name=<model_name> (e.g., --stt-arg model_name=large-v3). However, only the respective default models are packaged in the docker image, so it will start to download the model weights on container start.
:test_tube: Create your own client
You can also write your own client from scratch and connect it to our joinly MCP server. See client_example.py for a starting point.
The joinly MCP server provides following tools and resources:
Tools
join_meeting- Join meeting with URL, participant name, and optional passcodeleave_meeting- Leave the current meetingspeak_text- Speak text using TTS (requirestextparameter)send_chat_message- Send chat message (requiresmessageparameter)mute_yourself- Mute microphoneunmute_yourself- Unmute microphoneget_chat_history- Get current meeting chat history in JSON format- more soon…
Resources
transcript://live- Live meeting transcript in JSON format. Subscribable for real-time updates when new utterances are added.
:building_construction: Developing joinly.ai
For development we recommend using the development container, which installs all necessary dependencies. To get started, install the DevContainer Extension for Visual Studio Code, open the repository and choose Reopen in Container.
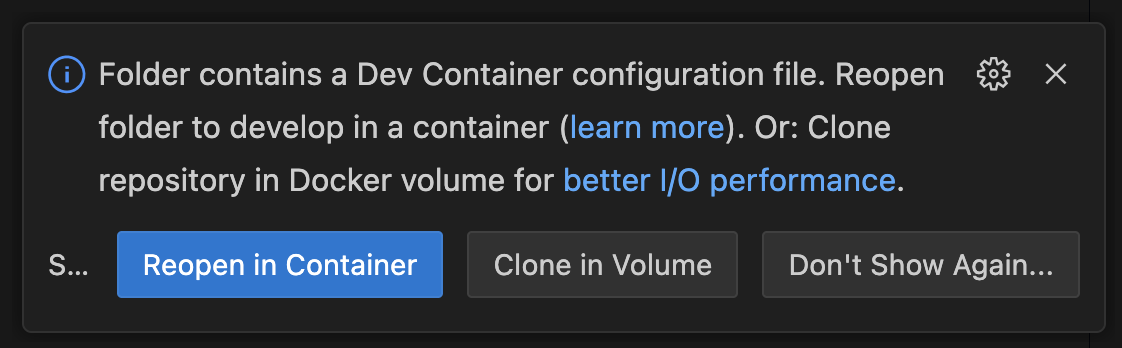
The installation can take some time, since it downloads all packages as well as models for Whisper/Kokoro and the Chromium browser. At the end, it automatically invokes the download_assets.py script. If you see errors like Missing kokoro-v1.0.onnx, run this script manually using:
uv run scripts/download_assets.py
We’d love to see what you are using it for or building with it. Showcase your work on our discord
:pencil2: Roadmap
Meeting
- [ ] Camera in video call with status updates
- [ ] Enable screen share during video conferences
- [ ] Meeting chat as resource
- [ ] Participant metadata and joining/leaving
- [ ] Improve browser agent capabilities
Conversation
- [ ] Improve client memory: reduce token usage, allow persistence across meetings
events - [ ] Improve End-of-Utterance/turn-taking detection
- [ ] Human approval mechanism from inside the meeting
- [ ] Speaker diarization
Integrations
- [ ] Showcase how to add agents using the A2A protocol
- [ ] Add more provider integrations (STT, TTS)
- [ ] Integrate meeting platform SDKs
- [ ] Add alternative open-source meeting provider
- [ ] Add support for Speech2Speech models
:busts_in_silhouette: Contributing
Contributions are always welcome! Feel free to open issues for bugs or submit a feature request. We’ll do our best to review all contributions promptly and help merge your changes.
Please check our Roadmap and don’t hesitate to reach out to us!
:memo: License
This project is licensed under the MIT License ‒ see the LICENSE file for details.
:speech_balloon: Getting help
If you have questions or feedback, or if you would like to chat with the maintainers or other community members, please use the following links: