- Explore MCP Servers
- layerzero_mcp
Layerzero Mcp
What is Layerzero Mcp
LayerZero OFT MCP is a TypeScript/Node.js Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed for creating, deploying, and bridging Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFTs) across multiple blockchains. It simplifies cross-chain interactions and token management using LayerZero’s protocols.
Use cases
Use cases include deploying OFTs for multi-chain DeFi platforms, creating interoperable tokens for gaming applications, and enabling seamless asset transfers across different blockchain networks.
How to use
To use layerzero_mcp, deploy the server and utilize the provided tools, such as ‘deploy-and-configure-oft-multichain’, to create and configure OFT contracts on LayerZero-supported chains. Parameters like token name, symbol, and total supply must be specified during deployment.
Key features
Key features include deterministic cross-chain contract addressing using Solidity’s CREATE2 opcode, easy integration with LLM agents and bots, and structured management of cross-chain token interactions.
Where to use
LayerZero OFT MCP can be used in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, cross-chain token projects, and any blockchain-based applications requiring secure and reliable cross-chain functionality.
Overview
What is Layerzero Mcp
LayerZero OFT MCP is a TypeScript/Node.js Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed for creating, deploying, and bridging Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFTs) across multiple blockchains. It simplifies cross-chain interactions and token management using LayerZero’s protocols.
Use cases
Use cases include deploying OFTs for multi-chain DeFi platforms, creating interoperable tokens for gaming applications, and enabling seamless asset transfers across different blockchain networks.
How to use
To use layerzero_mcp, deploy the server and utilize the provided tools, such as ‘deploy-and-configure-oft-multichain’, to create and configure OFT contracts on LayerZero-supported chains. Parameters like token name, symbol, and total supply must be specified during deployment.
Key features
Key features include deterministic cross-chain contract addressing using Solidity’s CREATE2 opcode, easy integration with LLM agents and bots, and structured management of cross-chain token interactions.
Where to use
LayerZero OFT MCP can be used in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, cross-chain token projects, and any blockchain-based applications requiring secure and reliable cross-chain functionality.
Content
LayerZero OFT MCP Server
LayerZero OFT MCP is a TypeScript/Node.js Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for creating, deploying, and bridging Omnichain Fungible Tokens (OFTs) across multiple blockchains. Interactions are primarily managed via ethers.js, leveraging LayerZero contracts and protocols for cross-chain communication.
This MCP abstracts the complexity of omnichain token creation and cross-chain interactions by providing a structured, context-aware layer for initiating, managing, and bridging OFTs. It is designed for easy integration with LLM agents, bots, or applications that require secure and reliable access to decentralized cross-chain functionality.
Deterministic Cross-Chain Contract Addressing
The MCP uses Solidity’s CREATE2 opcode to deploy OFT contracts at the same address on every chain.
The address is derived from the bytecode and a fixed salt, which includes currently the token name and symbol. Make sure you use unique identifiers when deploying, because you cannot create two times the same token (same name and symbol) using the same factory (You can also use an other type of salt if you want to avoid this).
It’s a working starting point. You can bring your own OFT contract and expand it with custom features or token logic. The system is open and extendable by design.
Features & Tools
This MCP server exposes the following tools for interaction:
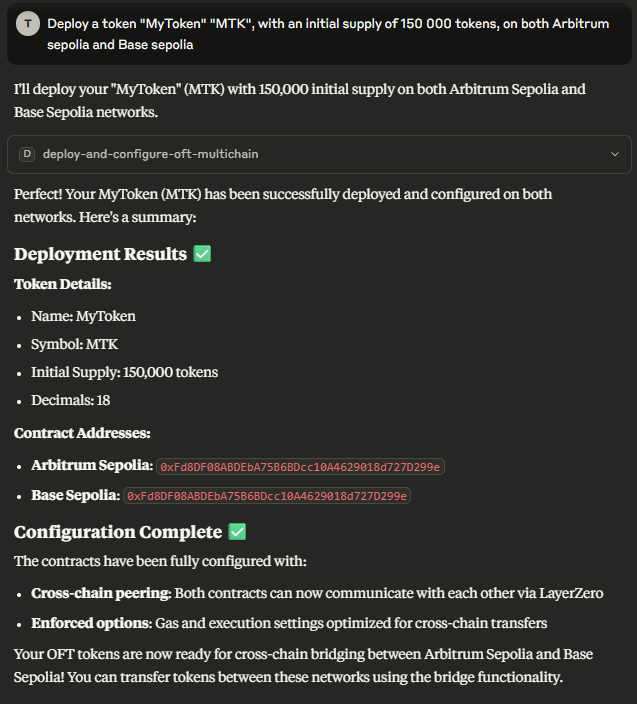
1. deploy-and-configure-oft-multichain
- Description: Deploys an Omnichain Fungible Token (OFT) contract to one or more specified LayerZero-supported chains. After successful deployments, it configures each new OFT contract to be a peer with all other newly deployed OFTs in the set. It also sets standard enforced options (e.g., for gas limits) on each contract to enable cross-chain transfers to its peers.
- Parameters:
tokenName(string): Name of the token (e.g., “MyToken”).tokenSymbol(string): Symbol of the token (e.g., “MYT”).initialTotalSupply(string): Total supply of the token in human-readable format (e.g., “1000000”). This will be parsed using thedecimalsvalue.decimals(number, Optional, default: 18): Number of decimals for the token.targetChains(array of strings): List of chain names (from the configuredNETWORKSinutils.ts, e.g.,["Arbitrum sepolia", "baseSepolia"]) to deploy and configure the OFT on. Must select at least one. For peering to occur, at least two chains must be specified and result in successful deployments.owner(string, Optional): The Ethereum address to be the owner of the deployed contracts. If not provided, defaults to theOWNER_ADDRESSset in the.envfile.
- Output: Details the success or failure of deployments on each target chain, peering status between them, and the status of setting enforced options.
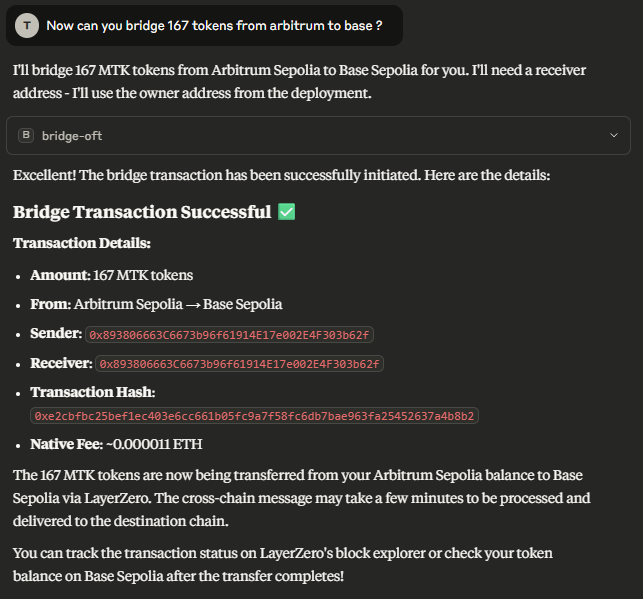
2. bridge-oft
- Description: Bridges OFT tokens from one chain to another using LayerZero.
- Parameters:
tokenAddress(string): The address of the OFT contract on the source chain.amount(string): The amount of tokens to bridge (e.g., “100”). This is parsed assuming 18 decimals; ensure your token uses this or modify the tool if necessary.fromChain(string): The source chain name (e.g., “Arbitrum sepolia”).toChain(string): The destination chain name (e.g., “baseSepolia”).receiverAddress(string): The address to receive tokens on the destination chain.extraOptions(string, optional, default: “0x”): Extra options for LayerZero message execution.
- Output: Details of the bridging transaction, including the transaction hash.
IMPORTANT: Configure ABI and Bytecode
Before running the server, you MUST replace theses paths with the absolute path to your contract artifacts
// — index.ts —
// Replace these paths with the actual ABI and Bytecode JSON file of your OFT contract (e.g., from MyOFT.sol)
const oftPath = resolve(
"D:\\Dev\\layerzero-mcp\\artifacts\\MyOFT\\MyOFT.json"
);
// Same here for the factory contract
// This should point to the CREATE2Factory ABI and Bytecode JSON file
const factoryPath = resolve(
"D:\\Dev\\layerzero-mcp\\artifacts\\factory\\CREATE2Factory.json"
);
// --- --- ---
Failure to do so will result in errors when attempting to use the deploy-and-configure-oft-multichain tool. The bridge-oft tool also requires the OFT_ABI to be correctly set for interacting with existing contracts.
Setup
Prerequisites
- Node.js (v16 or higher recommended)
- npm or yarn
- Access to an LLM or application that can communicate via the Model Context Protocol (e.g., Claude for Desktop).
Installation
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/your-username/layerzero-oft-mcp.git cd layerzero-oft-mcp -
Install dependencies:
npm install # or yarn install -
Create a
.envfile:
Copy the.env.example(if provided) or create a new.envfile in the root of the project and populate it with your details:PRIVATE_KEY="your_hex_encoded_private_key_here" OWNER_ADDRESS="your_owner_ethereum_address_here" ARBITRUM_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL="your_Arbitrum sepolia_testnet_rpc_url_here" BASE_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL="your_base_sepolia_testnet_rpc_url_here" ARBITRUM_FACTORY_ADDRESS="0x754a2643Ce68e0e34510B1E246254f93946AE3a1" BASE_FACTORY_ADDRESS="0x754a2643Ce68e0e34510B1E246254f93946AE3a1" # Add other RPC URL env variables if you configure more networks in utils.tsSecurity Note: Never commit your
.envfile containing private keys to a public repository. -
Update ABI and Bytecode:
As mentioned in the “IMPORTANT” section above, openlayerzero-mcp.tsand replaceOFT_ABIandOFT_BYTECODEplaceholders with your actual contract details. -
Build the project (if using TypeScript compilation):
npm run build # or yarn run build(This command assumes you have a
buildscript in yourpackage.jsonthat compiles TypeScript to JavaScript, e.g.,tsc)
Configure the MCP for Claude for Desktop (Example)
Add the MCP configuration to your Claude for Desktop configuration file (typically found at C:\Users\{User}\AppData\Roaming\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json on Windows):
{
"layerzero-oft-mcp": {
"command": "node",
"args": [
"<PROJECT_ABSOLUTE_FILEPATH>/build/index.js"
],
"env": {
"PRIVATE_KEY": "your_hex_encoded_private_key_here",
"OWNER_ADDRESS": "your_owner_ethereum_address_here",
"ARBITRUM_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL": "your_Arbitrum_sepolia_testnet_rpc_url_here",
"BASE_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL": "your_base_sepolia_testnet_rpc_url_here",
"ARBITRUM_FACTORY_ADDRESS": "0x754a2643Ce68e0e34510B1E246254f93946AE3a1",
"BASE_FACTORY_ADDRESS": "0x754a2643Ce68e0e34510B1E246254f93946AE3a1"
}
}
}- Replace
<PROJECT_ABSOLUTE_FILEPATH>with the actual absolute path to your project directory. - Ensure the
envvariables here match those required by your server, or that they are correctly picked up from your.envfile if your Node.js setup loads them (thedotenv.config()call in the scripts should handle this). For Claude Desktop, explicitly setting them inclaude_desktop_config.jsonis required.
Follow the official MCP guide for more details on testing with Claude for Desktop.
Running the Application & Example Usage
Once configured (including ABI/Bytecode and environment variables), the MCP server will be launched by the host application (e.g., Claude for Desktop) when needed.
You can then interact with it using natural language prompts if using an LLM. For example:
To deploy and configure a new OFT:
“Deploy a new OFT named ‘OmniCoin’ (OMC) with a total supply of 500,000 tokens across both Arbitrum sepolia and Base Sepolia testnets.”
This will use the deploy-and-configure-oft-multichain tool.
To bridge existing OFT tokens:
“Bridge 50 MyOFT from Arbitrum sepolia to Base Sepolia to address 0x123…abc. The token is deployed at 0xabc…123 on Arbitrum sepolia.”
This will use the bridge-oft tool.
NOTE: Ensure you have sufficient gas tokens (e.g., testnet ETH or MATIC) on the respective chains for the account associated with your PRIVATE_KEY to cover deployment and bridging transaction fees.
Example Screenshots
Deploying an OFT
Bridging an OFT