- Explore MCP Servers
- mcp-inspect
Mcp Inspect
What is Mcp Inspect
MCP Remote Inspect is a minimal, client-only tool designed to inspect real-time message exchanges between an MCP Client and a remote MCP Server. Unlike the official inspector, it does not require a local proxy server, allowing for instant use through a web browser.
Use cases
It is suited for users who need to analyze the actual message flow between an MCP Client and a remote MCP Server, debug protocol issues, or understand the full range of message types exchanged. It is also useful for developers who wish to test CORS settings without needing the overhead of a local environment.
How to use
Users can access the live demo by visiting the provided URL. They simply need to enter the MCP Server URL, choose the transport type, and connect to the server. After making calls to tools, they can view and copy the raw results along with all exchanged messages. Alternatively, developers can run the application locally or build it for production using npm commands.
Key features
Key features include direct connection to any MCP Server endpoint, visibility of real endpoints and messages (including heartbeats), support for Streamable HTTP mode, and the display of actual JSON responses, bypassing any proxy masking that may occur in other tools.
Where to use
This tool should be used when real-time monitoring of message exchanges is necessary, especially for protocol debugging, CORS testing, and gaining insights into the actual client/server interactions without the complications of a proxy environment.
Overview
What is Mcp Inspect
MCP Remote Inspect is a minimal, client-only tool designed to inspect real-time message exchanges between an MCP Client and a remote MCP Server. Unlike the official inspector, it does not require a local proxy server, allowing for instant use through a web browser.
Use cases
It is suited for users who need to analyze the actual message flow between an MCP Client and a remote MCP Server, debug protocol issues, or understand the full range of message types exchanged. It is also useful for developers who wish to test CORS settings without needing the overhead of a local environment.
How to use
Users can access the live demo by visiting the provided URL. They simply need to enter the MCP Server URL, choose the transport type, and connect to the server. After making calls to tools, they can view and copy the raw results along with all exchanged messages. Alternatively, developers can run the application locally or build it for production using npm commands.
Key features
Key features include direct connection to any MCP Server endpoint, visibility of real endpoints and messages (including heartbeats), support for Streamable HTTP mode, and the display of actual JSON responses, bypassing any proxy masking that may occur in other tools.
Where to use
This tool should be used when real-time monitoring of message exchanges is necessary, especially for protocol debugging, CORS testing, and gaining insights into the actual client/server interactions without the complications of a proxy environment.
Content
MCP Remote Inspect
A minimal, browser-based tool for inspecting real, raw message exchanges between an MCP Client and a remote MCP Server. Unlike the official @modelcontextprotocol/inspector, this project is client-only—no local proxy server required. You can use it instantly 👉 HERE.
flowchart TD subgraph Official_Inspector["@modelcontextprotocol/inspector"] C[MCP Client] <--> D["[Proxy MCP Server] <br> Local Proxy <br> [Proxy MCP Client]"] <--> E[MCP Server] end subgraph This_Project["mcp-inspect.vercel.app"] A[MCP Client] <--> B[MCP Server] end
https://mcp-inspect.vercel.app
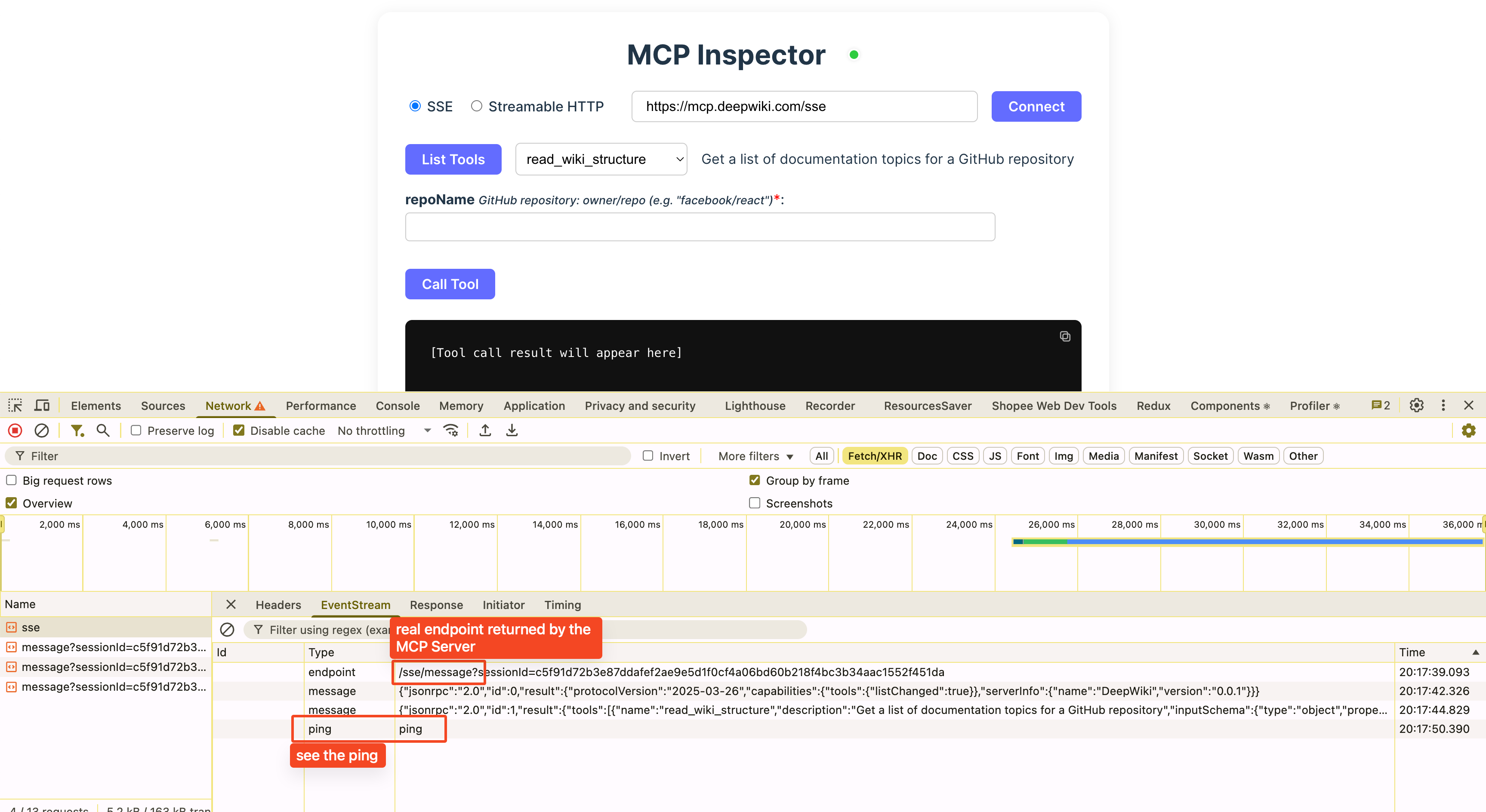
@modelcontextprotocol/inspector
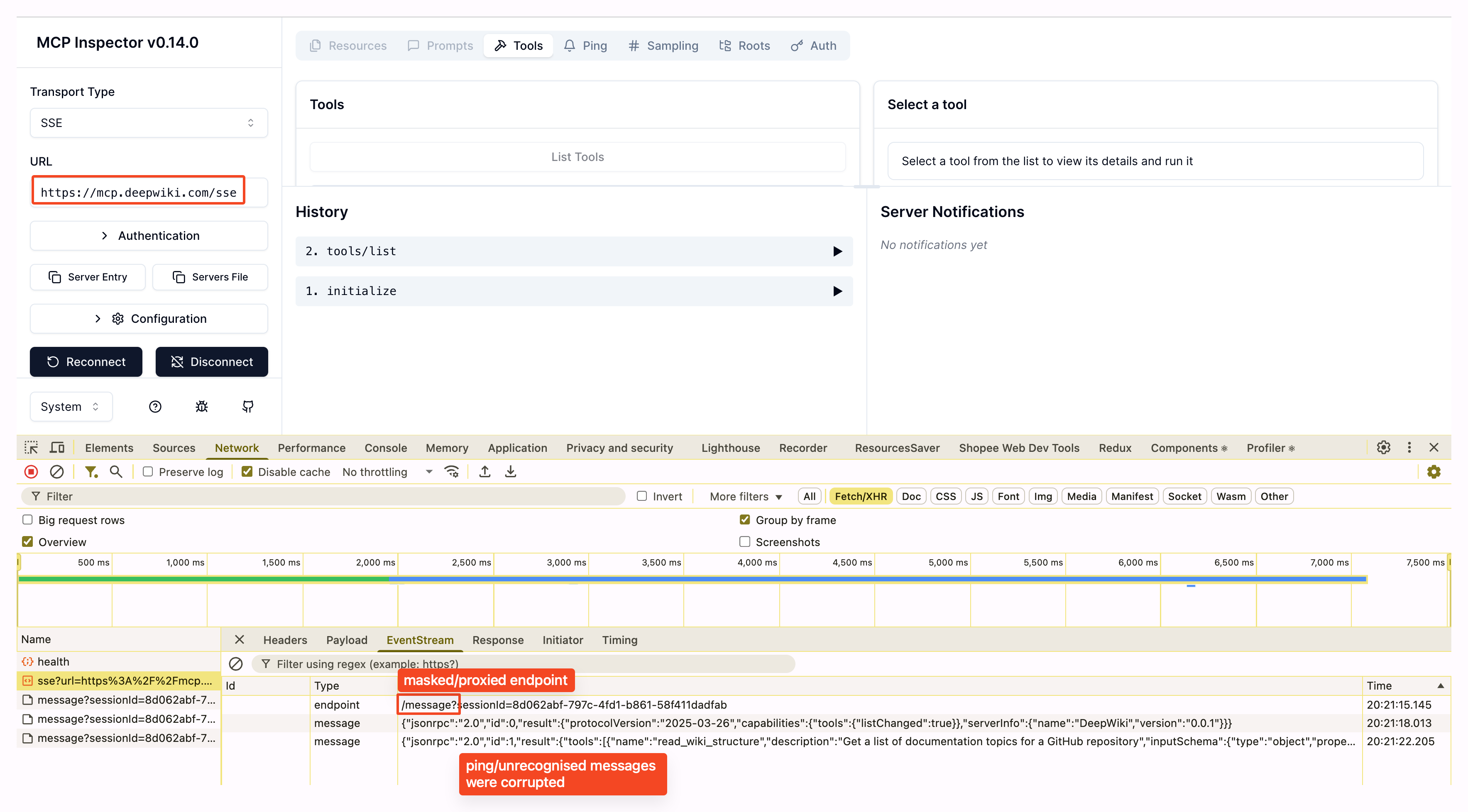
Key Features & Differences
- Direct-to-Server: Connects directly to any MCP Server endpoint (SSE or Streamable HTTP), so you see the real messages and endpoints—no proxy masking.
- Raw Endpoint Visibility: If the server sends a message to
/mcp/message, you’ll see/mcp/message(not/messageas with the official inspector’s proxy). - Heartbeat/Ping Support: All messages, including server heartbeats (ping), are visible. The official inspector hides these.
- Streamable HTTP Mode: If the server uses
enableJsonResponse=true, you’ll see the actual JSON response. The official inspector always showstext/event-stream(from its proxy), not the real server response.
Limitations
- Tools-Only Focus: Only supports the Tools use case (SSE and Streamable HTTP). Does not support STDIO, Prompts, Resources, etc.
- CORS: As a browser app, it is subject to CORS restrictions. If the MCP Server does not allow cross-origin requests, you may not be able to connect. Unlike the official inspector, there is no local proxy to bypass CORS.
When to Use This
- You want to see the real message flow between your MCP Client and a remote MCP Server.
- You want to debug or understand the actual protocol, endpoints, and message types (including heartbeats/pings).
- You don’t want to install or run @modelcontextprotocol/inspector, just access an MCP Inspector directly.
How to Use
1. Use the Live Demo
Just open https://mcp-inspect.vercel.app in your browser.
- Enter your MCP Server URL (examples:
https://mcp.deepwiki.com/ssefor SSE,https://mcp.context7.com/mcpfor Streamable HTTP). - Choose the transport type (SSE or Streamable HTTP).
- Connect, list tools, select a tool, fill in parameters, and call the tool.
- View and copy the raw results and all exchanged messages.
- Tip: Open your browser’s DevTools Network tab to see the real HTTP requests and responses exchanged directly with the MCP server—no proxy, no masking.
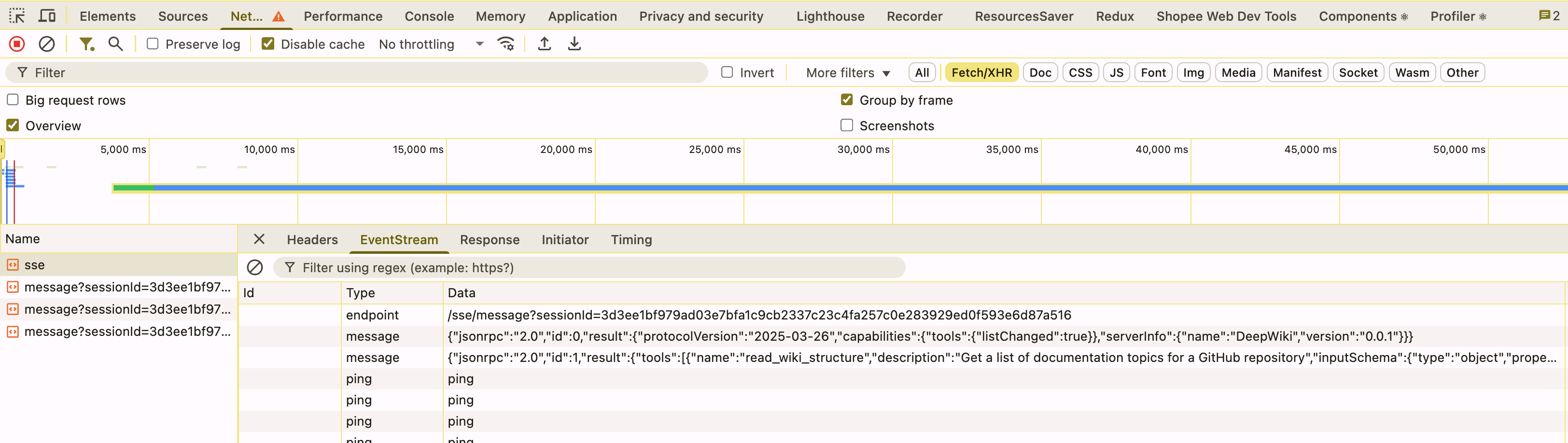
2. Run Locally (for development)
npm install npm run dev
Then open http://localhost:5173 in your browser.
3. Build for Production
npm run build
Why Not Use the Official Inspector?
- The official
modelcontextprotocol/inspectorruns a local proxy server, so you only see messages as they pass through the proxy—not the real server endpoints or all message types. - This project is ideal for protocol debugging, CORS testing, and understanding the actual MCP Client/Server exchange.
Message Exchange in Different Transport Types
I. STDIO
sequenceDiagram participant Client participant Server Note over Client,Server: 1. Start Server as Subprocess Client->>+Server: [spawn process, open stdin/stdout] Note over Client,Server: 2. Tool Discovery (Initialization) Client-->>+Server: stdin: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"initialize", ...}\n\n Server-->>-Client: stdout: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "id":..., "result": ...}\n\n Client-->>+Server: stdin: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"notifications/initialized", ...}\n\n Client-->>+Server: stdin: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/list", ...}\n\n Server-->>-Client: stdout: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "id":..., "result": ...}\n\n Note over Client,Server: 3. Tool Call Client-->>+Server: stdin: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/call", ...}\n\n Server-->>-Client: stdout: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "id":..., "result": ...}\n\n Note over Client,Server: ... Client->>Server: [close stdin to terminate]
II. SSE (Deprecated)
sequenceDiagram participant Client participant Server Note over Client,Server: 1. Establish SSE Connection Client->>+Server: GET /sse Server-->>+Client: 200 OK Server-->>-Client: SSE: event: endpoint\ndata: /messages?sessionId=... Note over Client,Server: 2. Tool Discovery (Initialization) Client->>+Server: POST /messages?sessionId=...\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"initialize", ...} Server->>Client: 202 Accepted Server-->>-Client: SSE: event: message\ndata: {"id":..., "result": ...} Client->>+Server: POST /messages?sessionId=...\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"notifications/initialized", ...} Server->>-Client: 202 Accepted Client->>+Server: POST /messages?sessionId=...\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/list", ...} Server->>Client: 202 Accepted Server-->>-Client: SSE: event: message\ndata: {"id":..., "result": ...} Note over Client,Server: 3. Tool Call Client->>+Server: POST /messages?sessionId=...\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/call", ...} Server->>Client: 202 Accepted Server-->>-Client: SSE: event: message\ndata: {"id":..., "result": ...} Note over Client,Server: ... Client->>Server: [close connection]
III. Streamable HTTP
1. Direct JSON Response in POST
The server replies to the POST request with a standard JSON body. Used for “API wrapper” servers.
sequenceDiagram participant Client participant Server Note over Client,Server: 1. Session Initialization Client->>+Server: POST /mcp\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"initialize", ...} Server->>-Client: 200 OK\nHeaders: content-type: application/json\nBody: {"id":..., "result": ...} Note over Client,Server: 2. Tool Call Client->>+Server: POST /mcp\nHeaders: content-type: application/json\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/call", ...} Server->>-Client: 200 OK\nHeaders: content-type: application/json\nBody: {"id":..., "result": ...}
2. Streaming Response in POST (SSE in POST)
The server replies to the POST request with a streaming response using Content-Type: text/event-stream. The client reads the stream from the POST response body.
sequenceDiagram participant Client participant Server Note over Client,Server: 1. Session Initialization Client->>+Server: POST /mcp\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"initialize", ...} Server-->>-Client: 200 OK\nHeaders: content-type: text/event-stream\nBody: {"id":..., "result": ...} Note over Client,Server: 2. Tool Call (Streaming) Client->>+Server: POST /mcp\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/call", ...} Server-->>-Client: 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/event-stream\nSSE: event:message\ndata: {"id":..., "result": ...}
3. Streaming Response via Persistent SSE Channel (GET /mcp)
The server replies to the POST with an acknowledgment (often 202 Accepted), and delivers the actual results asynchronously over a persistent SSE stream (opened via GET /mcp).
sequenceDiagram participant Client participant Server Note over Client,Server: 1. Session Initialization Client->>+Server: POST /mcp\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"initialize", ...} Server-->>-Client: 200 OK\nHeaders: mcp-session-id: <sessionId>\nBody: {"id":..., "result": ...} (application/json) Note over Client,Server: 2. Open Persistent SSE Channel Client->>+Server: GET /mcp\nHeaders: mcp-session-id: <sessionId>, Accept: text/event-stream Server-->>-Client: 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/event-stream Note over Client,Server: 3. Tool Call (Async) Client->>+Server: POST /mcp\nHeaders: mcp-session-id: <sessionId>\nBody: {"jsonrpc":"2.0", "method":"tools/call", ...} Server-->>-Client: 202 Accepted Server-->>+Client: SSE: event:message\ndata: {"id":..., "result": ...} (delivered on SSE channel) Note over Client,Server: 4. Resuming Stream (SSE Reconnect) Client->>+Server: GET /mcp\nHeaders: mcp-session-id: <sessionId>, Accept: text/event-stream, Last-Event-Id: <lastEventId> Server-->>-Client: 200 OK\nContent-Type: text/event-stream\nSSE: event:message\ndata: {"id":..., "result": ...} (resumed)
License
MIT
