- Explore MCP Servers
- mcp-server-commands
Mcp Server Commands
What is Mcp Server Commands
mcp-server-commands is a Model Context Protocol server designed to execute commands and scripts, enabling interaction with LLMs (Large Language Models) like Claude.
Use cases
Use cases include automating tasks through scripts, generating dynamic content with LLMs, and providing command output in chat applications.
How to use
To use mcp-server-commands, install the dependencies via npm, build the server, and configure it with the Claude Desktop app. Commands can be run using the ‘run_command’ and ‘run_script’ functionalities.
Key features
Key features include the ability to run shell commands and scripts, return standard output and error messages, and integrate with LLMs for dynamic code execution.
Where to use
mcp-server-commands can be utilized in software development, AI applications, and any environment where command execution and LLM interaction are required.
Clients Supporting MCP
The following are the main client software that supports the Model Context Protocol. Click the link to visit the official website for more information.
Overview
What is Mcp Server Commands
mcp-server-commands is a Model Context Protocol server designed to execute commands and scripts, enabling interaction with LLMs (Large Language Models) like Claude.
Use cases
Use cases include automating tasks through scripts, generating dynamic content with LLMs, and providing command output in chat applications.
How to use
To use mcp-server-commands, install the dependencies via npm, build the server, and configure it with the Claude Desktop app. Commands can be run using the ‘run_command’ and ‘run_script’ functionalities.
Key features
Key features include the ability to run shell commands and scripts, return standard output and error messages, and integrate with LLMs for dynamic code execution.
Where to use
mcp-server-commands can be utilized in software development, AI applications, and any environment where command execution and LLM interaction are required.
Clients Supporting MCP
The following are the main client software that supports the Model Context Protocol. Click the link to visit the official website for more information.
Content
Tools
Tools are for LLMs to request. Claude Sonnet 3.5 intelligently uses run_command. And, initial testing shows promising results with Groq Desktop with MCP and llama4 models.
Currently, just one command to rule them all!
run_command- run a command, i.e.hostnameorls -alorecho "hello world"etc- Returns
STDOUTandSTDERRas text - Optional
stdinparameter means your LLM can- pass code in
stdinto commands likefish,bash,zsh,python - create files with
cat >> foo/bar.txtfrom the text instdin
- pass code in
- Returns
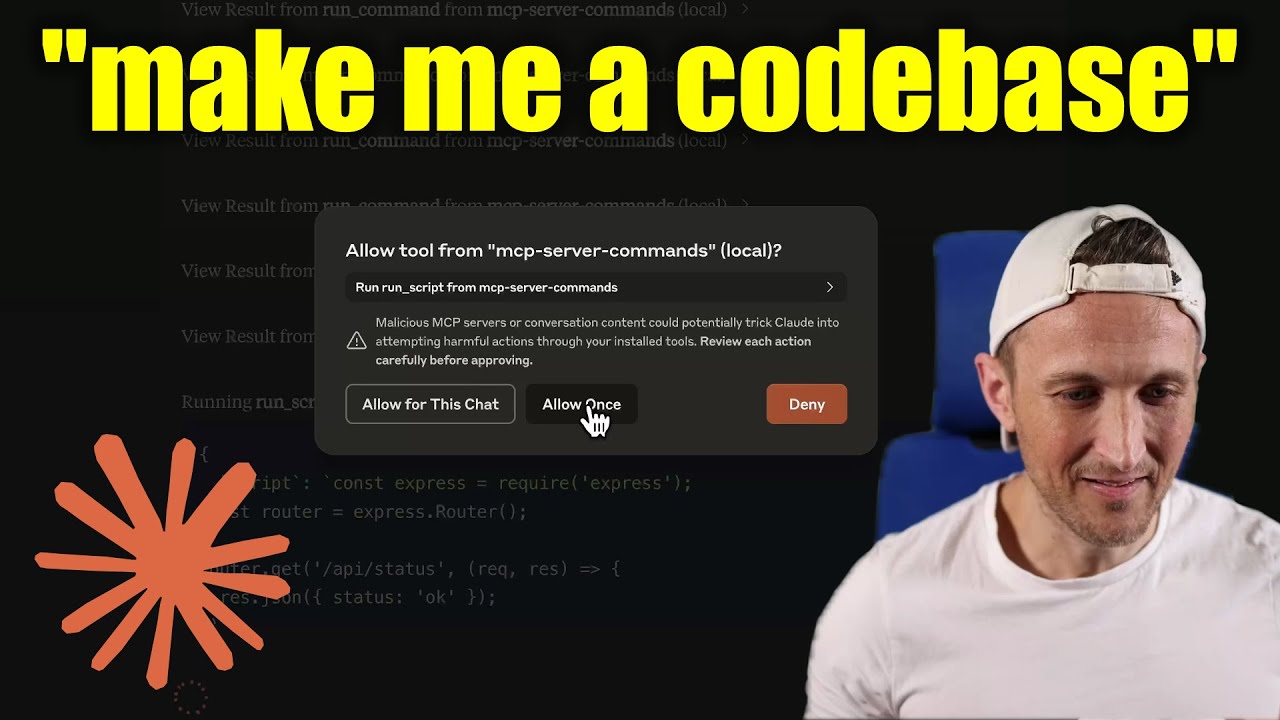
[!WARNING]
Be careful what you ask this server to run!
In Claude Desktop app, useApprove Once(notAllow for This Chat) so you can review each command, useDenyif you don’t trust the command.
Permissions are dictated by the user that runs the server.
DO NOT run withsudo.
Video walkthrough
Prompts
Prompts are for users to include in chat history, i.e. via Zed’s slash commands (in its AI Chat panel)
run_command- generate a prompt message with the command output
Development
Install dependencies:
npm install
Build the server:
npm run build
For development with auto-rebuild:
npm run watch
Installation
To use with Claude Desktop, add the server config:
On MacOS: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
On Windows: %APPDATA%/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
Groq Desktop (beta, macOS) uses ~/Library/Application Support/groq-desktop-app/settings.json
Use the published npm package
Published to npm as mcp-server-commands using this workflow
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-server-commands": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-server-commands"
]
}
}
}Use a local build (repo checkout)
Make sure to run npm run build
Local Models
- Most models are trained such that they don’t think they can run commands for you.
- Sometimes, they use tools w/o hesitation… other times, I have to coax them.
- Use a system prompt or prompt template to instruct that they should follow user requests. Including to use
run_commandswithout double checking.
- Ollama is a great way to run a model locally (w/ Open-WebUI)
# NOTE: make sure to review variants and sizes, so the model fits in your VRAM to perform well!
# Probably the best so far is [OpenHands LM](https://www.all-hands.dev/blog/introducing-openhands-lm-32b----a-strong-open-coding-agent-model)
ollama pull https://huggingface.co/lmstudio-community/openhands-lm-32b-v0.1-GGUF
# https://ollama.com/library/devstral
ollama pull devstral
# Qwen2.5-Coder has tool use but you have to coax it
ollama pull qwen2.5-coder
HTTP / OpenAPI
The server is implemented with the STDIO transport.
For HTTP, use mcpo for an OpenAPI compatible web server interface.
This works with Open-WebUI
uvx mcpo --port 3010 --api-key "supersecret" -- npx mcp-server-commands
# uvx runs mcpo => mcpo run npx => npx runs mcp-server-commands
# then, mcpo bridges STDIO <=> HTTP
[!WARNING]
I briefly usedmcpowithopen-webui, make sure to vet it for security concerns.
Logging
Claude Desktop app writes logs to ~/Library/Logs/Claude/mcp-server-mcp-server-commands.log
By default, only important messages are logged (i.e. errors).
If you want to see more messages, add --verbose to the args when configuring the server.
By the way, logs are written to STDERR because that is what Claude Desktop routes to the log files.
In the future, I expect well formatted log messages to be written over the STDIO transport to the MCP client (note: not Claude Desktop app).
Debugging
Since MCP servers communicate over stdio, debugging can be challenging. We recommend using the MCP Inspector, which is available as a package script:
npm run inspector
The Inspector will provide a URL to access debugging tools in your browser.
Dev Tools Supporting MCP
The following are the main code editors that support the Model Context Protocol. Click the link to visit the official website for more information.