- Explore MCP Servers
- pandoc
Pandoc Document Conversion
What is Pandoc Document Conversion
mcp-pandoc is a Model Context Protocol server designed for document format conversion using pandoc. It allows users to transform content between various document formats while retaining the original formatting and structure. Currently, it is in early development with PDF support and other functionalities still being enhanced.
Use cases
mcp-pandoc can be used in scenarios where users need to convert documents from one format to another, such as transforming markdown files to PDF, HTML, or other formats. It is particularly useful for writers, educators, and developers who require flexible document format handling.
How to use
To use mcp-pandoc, users must first ensure that the necessary dependencies like pandoc and the uv package are installed. After configuration, users can execute commands to convert content or files by specifying inputs and outputs. Proper file paths must be provided for advanced formats.
Key features
Key features include support for multiple document formats (e.g., markdown, HTML, PDF, DOCX), the ability to convert both direct content and files, and advanced formatting options. The tool emphasizes preserving document structure during conversion.
Where to use
mcp-pandoc is intended for use in environments requiring document conversion capabilities, such as academic settings, content management systems, and software development projects where document format compatibility is needed.
Overview
What is Pandoc Document Conversion
mcp-pandoc is a Model Context Protocol server designed for document format conversion using pandoc. It allows users to transform content between various document formats while retaining the original formatting and structure. Currently, it is in early development with PDF support and other functionalities still being enhanced.
Use cases
mcp-pandoc can be used in scenarios where users need to convert documents from one format to another, such as transforming markdown files to PDF, HTML, or other formats. It is particularly useful for writers, educators, and developers who require flexible document format handling.
How to use
To use mcp-pandoc, users must first ensure that the necessary dependencies like pandoc and the uv package are installed. After configuration, users can execute commands to convert content or files by specifying inputs and outputs. Proper file paths must be provided for advanced formats.
Key features
Key features include support for multiple document formats (e.g., markdown, HTML, PDF, DOCX), the ability to convert both direct content and files, and advanced formatting options. The tool emphasizes preserving document structure during conversion.
Where to use
mcp-pandoc is intended for use in environments requiring document conversion capabilities, such as academic settings, content management systems, and software development projects where document format compatibility is needed.
Content
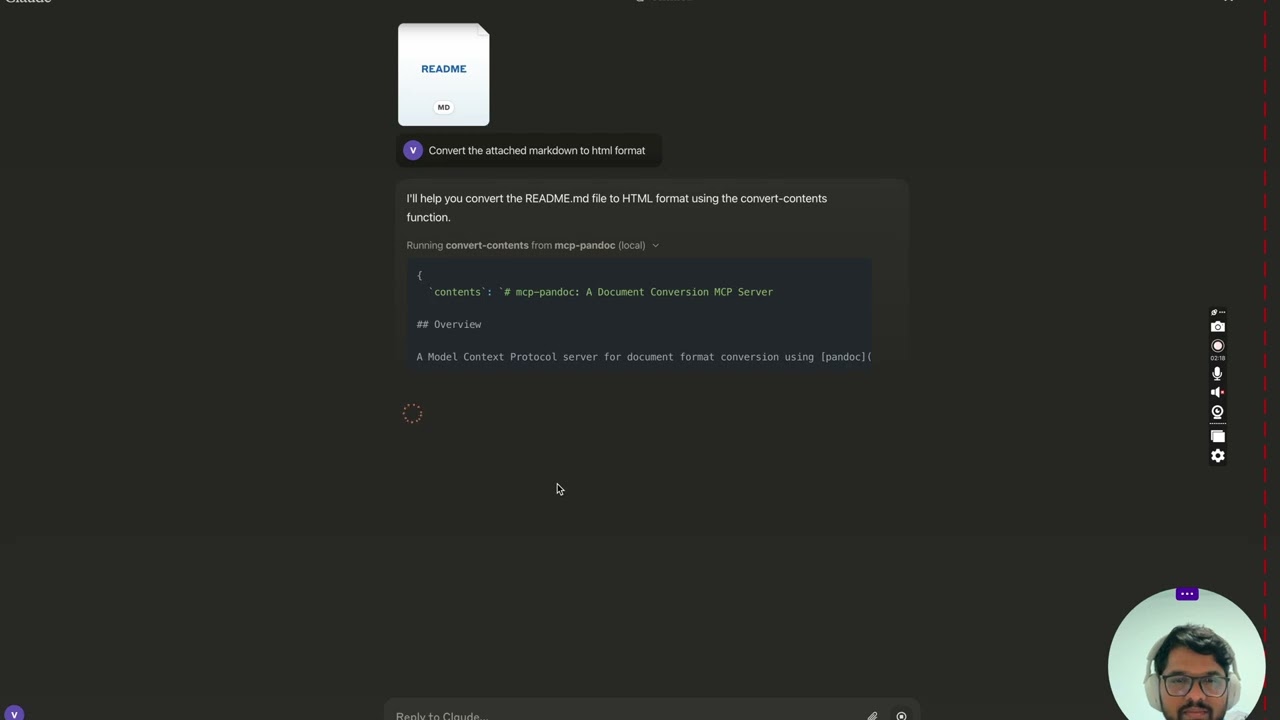
mcp-pandoc: A Document Conversion MCP Server
Officially included in the Model Context Protocol servers open-source project. 🎉
Overview
A Model Context Protocol server for document format conversion using pandoc. This server provides tools to transform content between different document formats while preserving formatting and structure.
Please note that mcp-pandoc is currently in early development. PDF support is under development, and the functionality and available tools are subject to change and expansion as we continue to improve the server.
Credit: This project uses the Pandoc Python package for document conversion, forming the foundation for this project.
Demo
Screenshots
More to come…
Tools
convert-contents- Transforms content between supported formats
- Inputs:
contents(string): Source content to convert (required if input_file not provided)input_file(string): Complete path to input file (required if contents not provided)input_format(string): Source format of the content (defaults to markdown)output_format(string): Target format (defaults to markdown)output_file(string): Complete path for output file (required for pdf, docx, rst, latex, epub formats)
- Supported input/output formats:
- markdown
- html
- docx
- rst
- latex
- epub
- txt
- Note: For advanced formats (pdf, docx, rst, latex, epub), an output_file path is required
Supported Formats
Currently supported formats:
Basic formats (direct conversion):
- Plain text (.txt)
- Markdown (.md)
- HTML (.html)
Advanced formats (requires complete file paths):
- PDF (.pdf) - requires TeX Live installation
- DOCX (.docx)
- RST (.rst)
- LaTeX (.tex)
- EPUB (.epub)
Note: For advanced formats:
- Complete file paths with filename and extension are required
- PDF conversion requires TeX Live installation (see Critical Requirements section -> For macOS:
brew install texlive) - When no output path is specified:
- Basic formats: Displays converted content in the chat
- Advanced formats: May save in system temp directory (/tmp/ on Unix systems)
Usage & configuration
NOTE: Ensure to complete installing required packages mentioned below under “Critical Requirements”.
To use the published one
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-pandoc": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-pandoc"]
}
}
}
⚠️ Important Notes
Critical Requirements
- Pandoc Installation
- Required: Install
pandoc- the core document conversion engine - Installation:
# macOS brew install pandoc # Ubuntu/Debian sudo apt-get install pandoc # Windows # Download installer from: https://pandoc.org/installing.html - Verify:
pandoc --version
- UV package installation
- Required: Install
uvpackage (includesuvxcommand) - Installation:
# macOS brew install uv # Windows/Linux pip install uv - Verify:
uvx --version
- PDF Conversion Prerequisites: Only needed if you need to convert & save pdf
- TeX Live must be installed before attempting PDF conversion
- Installation commands:
# Ubuntu/Debian sudo apt-get install texlive-xetex # macOS brew install texlive # Windows # Install MiKTeX or TeX Live from: # https://miktex.org/ or https://tug.org/texlive/
- File Path Requirements
- When saving or converting files, you MUST provide complete file paths including filename and extension
- The tool does not automatically generate filenames or extensions
Examples
✅ Correct Usage:
# Converting content to PDF
"Convert this text to PDF and save as /path/to/document.pdf"
# Converting between file formats
"Convert /path/to/input.md to PDF and save as /path/to/output.pdf"
❌ Incorrect Usage:
# Missing filename and extension
"Save this as PDF in /documents/"
# Missing complete path
"Convert this to PDF"
# Missing extension
"Save as /documents/story"
Common Issues and Solutions
-
PDF Conversion Fails
- Error: “xelatex not found”
- Solution: Install TeX Live first (see installation commands above)
-
File Conversion Fails
- Error: “Invalid file path”
- Solution: Provide complete path including filename and extension
- Example:
/path/to/document.pdfinstead of just/path/to/
-
Format Conversion Fails
- Error: “Unsupported format”
- Solution: Use only supported formats:
- Basic: txt, html, markdown
- Advanced: pdf, docx, rst, latex, epub
Quickstart
Install
Option 1: Installing manually via claude_desktop_config.json config file
- On MacOS:
open ~/Library/Application\ Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - On Windows:
%APPDATA%/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
a) Only for local development & contribution to this repo
Development/Unpublished Servers Configuration
ℹ️ Replace
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-pandoc": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"<DIRECTORY>/mcp-pandoc",
"run",
"mcp-pandoc"
]
}
}
b) Published Servers Configuration - Consumers should use this config
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-pandoc": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"mcp-pandoc"
]
}
}
Option 2: To install Published Servers Configuration automatically via Smithery
Run the following bash command to install published mcp-pandoc pypi for Claude Desktop automatically via Smithery:
npx -y @smithery/cli install mcp-pandoc --client claude
- If you face any issue, use the “Published Servers Configuration” above directly instead of this cli.
Note: To use locally configured mcp-pandoc, follow “Development/Unpublished Servers Configuration” step above.
Development
Building and Publishing
To prepare the package for distribution:
- Sync dependencies and update lockfile:
uv sync
- Build package distributions:
uv build
This will create source and wheel distributions in the dist/ directory.
- Publish to PyPI:
uv publish
Note: You’ll need to set PyPI credentials via environment variables or command flags:
- Token:
--tokenorUV_PUBLISH_TOKEN - Or username/password:
--username/UV_PUBLISH_USERNAMEand--password/UV_PUBLISH_PASSWORD
Debugging
Since MCP servers run over stdio, debugging can be challenging. For the best debugging
experience, we strongly recommend using the MCP Inspector.
You can launch the MCP Inspector via npm with this command:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector uv --directory /Users/vivekvells/Desktop/code/ai/mcp-pandoc run mcp-pandoc
Upon launching, the Inspector will display a URL that you can access in your browser to begin debugging.
Contributing
We welcome contributions to enhance mcp-pandoc! Here’s how you can get involved:
- Report Issues: Found a bug or have a feature request? Open an issue on our GitHub Issues page.
- Submit Pull Requests: Improve the codebase or add features by creating a pull request.